Challenges Solved by WMS:
- Slow Information Consolidation: The system optimizes processes and ensures information is updated quickly and accurately.
- Data Entry Errors: Minimizes input errors through automated tools and support.
- Difficult Lot and FIFO Management: Simplifies tracking and managing lot and FIFO, improving warehouse efficiency.
- Location Management Challenges: Enables precise and flexible warehouse location control with its location management features.
- Errors in Outbound Operations (Mistakes, Shortages): Reduces errors during outbound processes, ensuring high accuracy.
- Inability to Trace Product Origins: Facilitates clear and detailed traceability from warehouse entry to exit.
Key Features of WMS:
- Real-time production management within the system.
- Operates import, export, and inventory tasks even during network or power outages.
- Supports HT-Webapp or Cloud.
- Utilizes QR Code technology.
- Operable on mobile devices.
- Cost-efficient.
- Manages Lot Numbers and FIFO.
- Simple and user-friendly interface.
- Handles planned and unplanned warehouse imports and exports.
- Manages multi-location warehouses without distance limitations.
- Flexible master configuration.
- Multi-language support on the web (English, Vietnamese, Japanese).
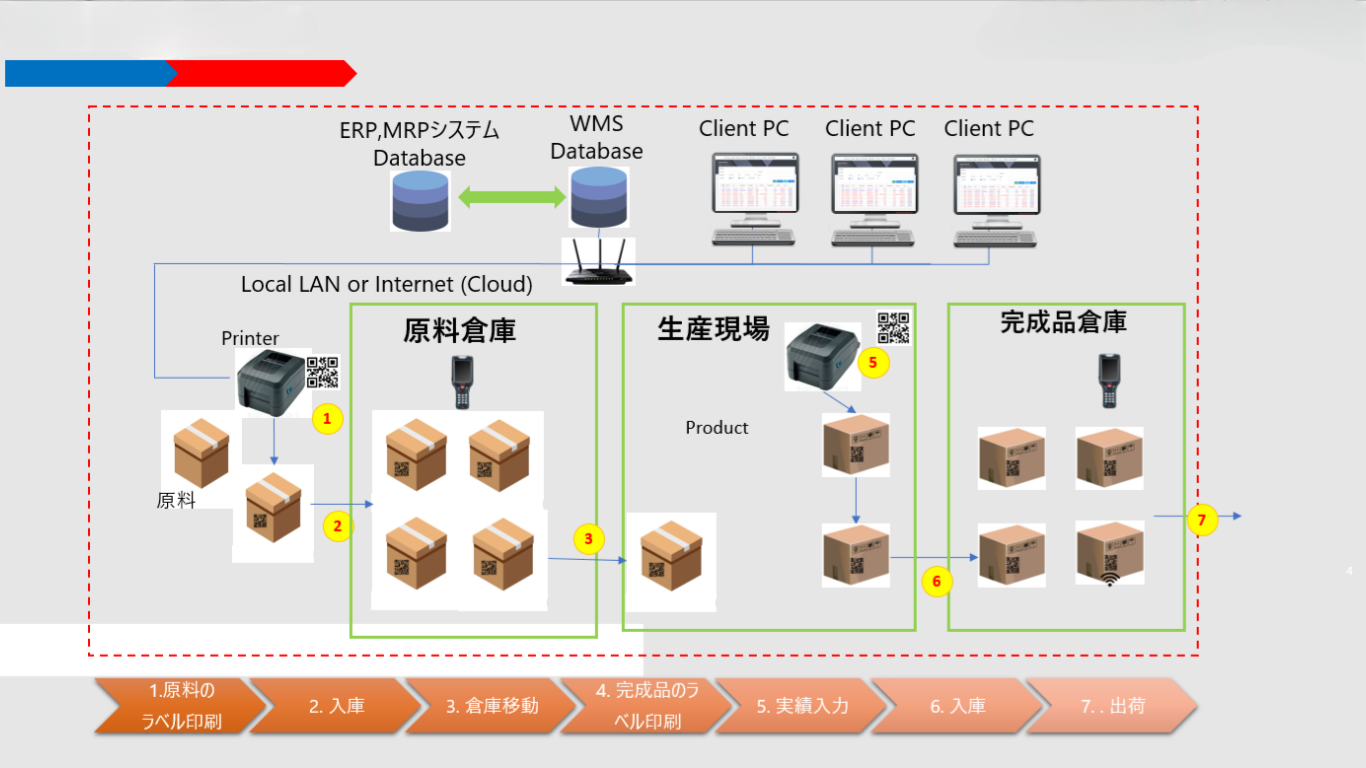
Workflow of WMS
Functions of WMS
1. Label Printing for Raw Materials, Semi-Finished Goods, and Finished Products
- Print labels for raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished products before warehouse entry.
- Batch printing capability.
- Prevent duplication of labels.
- Print individual product labels.
2. Managing Master Data for System Input
- Manage product catalog, BOM (Bill of Materials), production responsibility list, suppliers, and customers.
3. Purchase Order Management
- Manage customer purchase orders (PO).
- Track the status of purchase orders.
4. Order Management
- Manage order lists and track order statuses.
5. Goods Receipt (Inbound Operations)
- Receive goods by PO (planned goods receipt).
- Receive goods outside of PO (unplanned goods receipt).
- Adjust inventory on receipt.
6. Goods Issue (Outbound Operations)
- Two methods for outbound goods: planned shipment and unplanned shipment.
- Ship goods based on sales orders (SO) (planned shipments).
- Ship goods outside the plan (unplanned shipments).
- Adjust inventory during shipping.
7. Inventory Movement
- Transfer inventory between warehouses.
- Return raw materials to inventory.
- Move defective products (NG) to NG warehouse.
8. Finished Goods Receipt
- Receive finished goods from production area to finished goods warehouse.
- Receive products based on specific instructions (planned goods receipt).
- Receive products outside the plan (unplanned receipt).
- Receive goods returned by customers.
- Other types of inventory adjustment.
9. Outbound Goods (Shipping)
- Two methods for outbound goods: planned shipment and unplanned shipment.
- Ship goods based on sales orders (SO) (planned shipments).
- Ship goods outside the plan (unplanned shipments).
- Adjust inventory during shipping.
10. Inventory Adjustment
- Conduct inventory audits for raw materials, products, and finished goods.
- Perform inventory check using barcode scanners (by lot).
- Perform stock reconciliation (on computer).
- Automatic inventory adjustment.
- Update new inventory levels after adjustments.
11. Inventory List Management (Lot-based Management)
- Manage inventory by lot number.
- Display general inventory: total quantity of each item across warehouse locations.
- Display detailed inventory by lot: quantity of each item at specific warehouse locations, sorted by lot.
12. Offline Data Management
- In case of power failure or network issues, all inventory, movement, and shipping data will be stored locally on the HT device.
- Once the network connection is restored, simply press [Synchronize Data with Server], and all locally stored data will be uploaded to the server.
With S-WMS-R, businesses will have a comprehensive inventory management solution that is easy to operate and optimizes costs. The system improves work efficiency, reduces errors, and increases productivity, enabling companies to quickly respond to market changes.