1. What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses wireless communication to read and write data on RFID tags without contact from 50 cm to 10 meters.

2. RFID tag structure
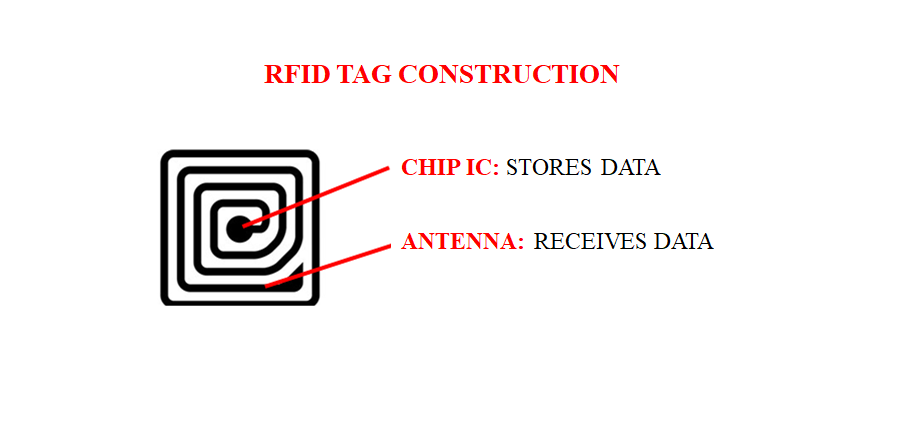
An RFID tag consists of two parts: an antenna that transmits and receives signals, and an RFID chip that stores information such as the tag ID, product name, manufacturer name, country of manufacture, date of manufacture, and expiration date of shipment. The simplest structure.
3. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
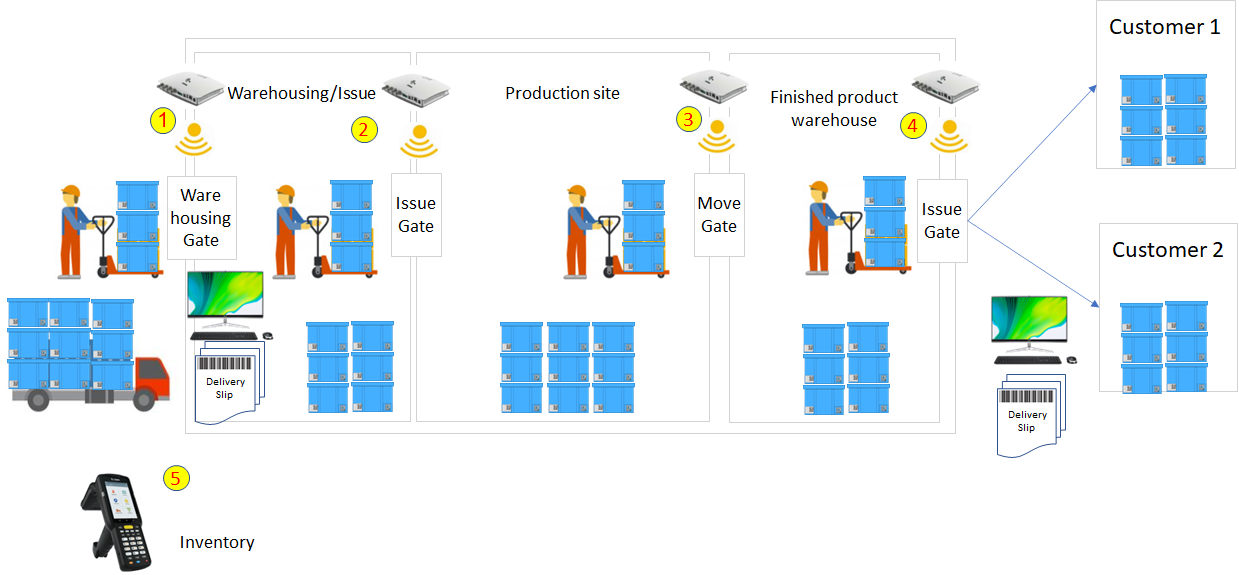
First, give each mobile asset an ID code. Data for each asset is stored in the system. When entering/exiting/moving warehouse, pass through the RFID reader (RFID scanning gate) of each warehouse. At that time, the movement information and storage location of each asset will be automatically updated to the system. At the time of delivery, after the assets go through the gate, a Delivery Slip is created (prints a list of the assets to be delivered). Delivery information will be stored in the system.
Inventory: Scan the RFID tag of the asset with a handy terminal to check the actual inventory quantity of the asset. The actual inventory quantity data is stored in the system.
After scanning, all information is automatically updated on the server without the need for document collection or data entry.
4. Strengths of RFID
Update data in real time

Enable to can at high speed

High precision


Easy to operate
Tags can be read even at long distances
5. FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEM
- Real-time asset warehouse management
- Asset location management (manage how much it is and where it is in the factory or at the customer’s location)
- Inventory
- Expired asset warning
- Maintenance history management

6. Equipment

Handy terminal :
Scan RFID

RFID scan machine :
Scan RFID in wide range

Laser Printer:
Print Delivery slip

Server:
Save the database

Computer :
Carry out administrative tasks

RFID tag



